Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Kosin Med J > Volume 28(1); 2013 > Article
-
Case Report
Two Cases of Increased Parasympathetic Nerve System in Irritable Bowel Syndrome with Diarrhea as a Predominant Symptom - Eui Kyu Kang, Jong Soon Choi
-
Kosin Medical Journal 2013;28(1):49-54.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.7180/kmj.2013.28.1.49
Published online: January 19, 2013
Department of Family Medicine, College of Medicine, Kosin University, Busan, Korea
- Corresponding author: Jong Soon Choi, Department of Family Medicine, College of Medicine, Kosin University, #34, Amnamdong, Suhgu, Busan 602-030, Korea Tel: +82-51-990-6476, E-mail: fmcjs@naver.com
• Received: July 25, 2012 • Accepted: September 28, 2012
Copyright © 2013 Kosin University School of Medicine Proceedings
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
- 1,187 Views
- 6 Download
- 2 Crossref
Abstract
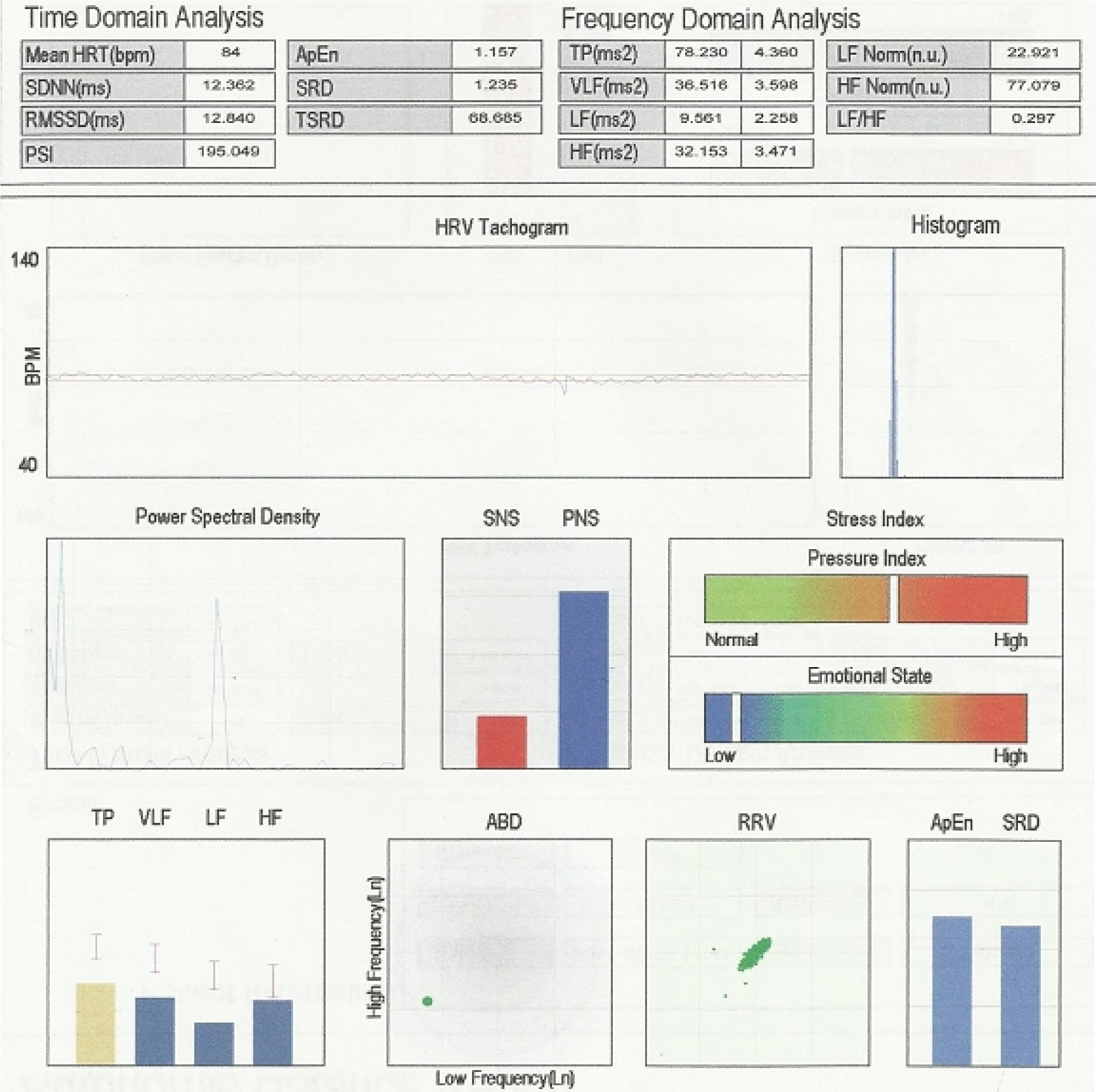
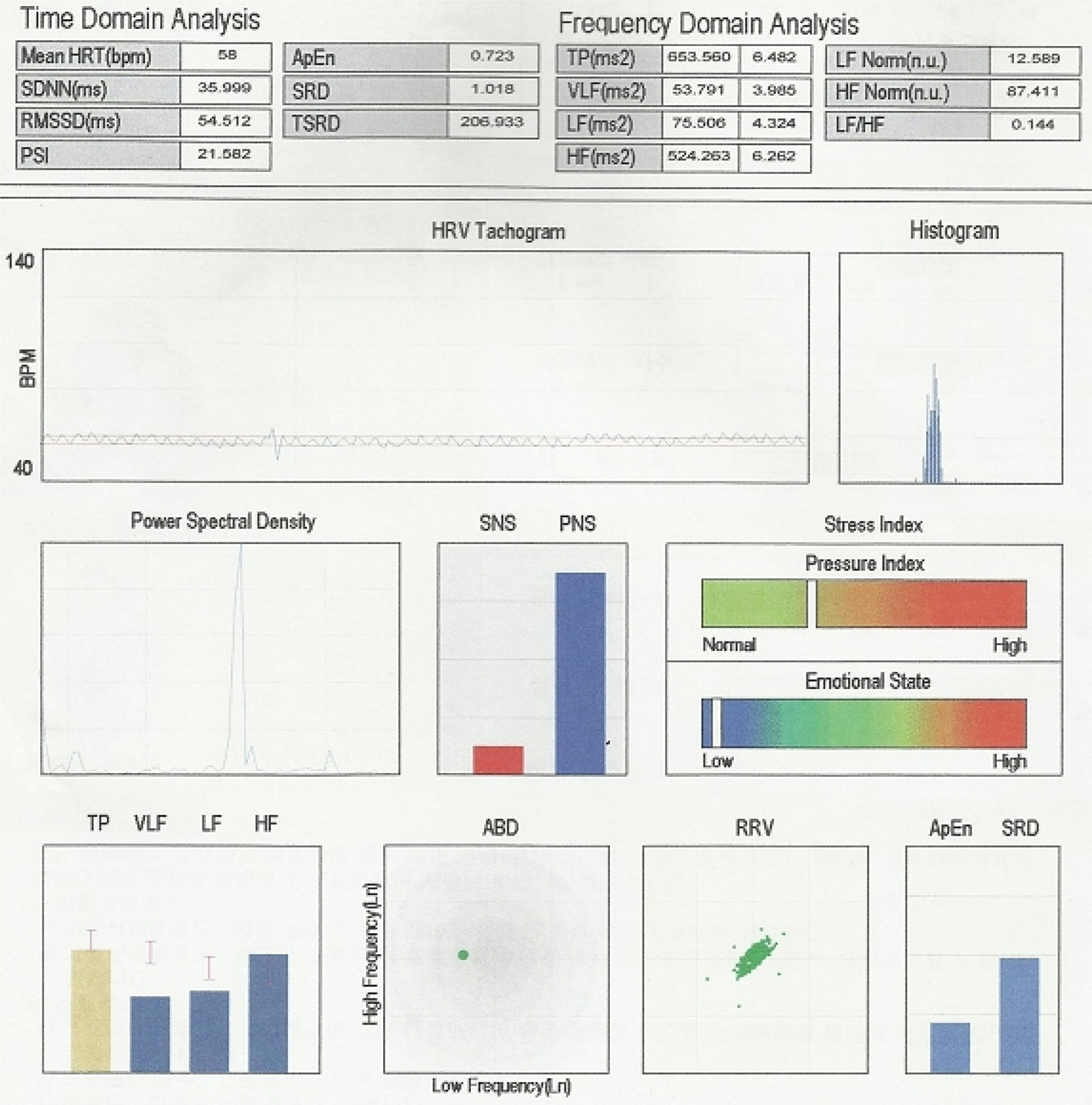
- The irritable bowel syndrome(IBS) is a chronic functional gastrointestinal disorder, characterized by abdominal pain, bloating and bowel disturbance. The pathophysiology of IBS is very complicated. Recent studies indicate that the most important mechanisms include visceral hypersensitivity, abnormal gut motility, autonomic nervous system(ANS) dysfunction and disorder of regulation of the brain-gut axis. Patients with IBS frequently present impaired autonomic regulation. Heart rate variability(HRV) is an acknowledged tool for estimating autonomic function. We experienced two cases of increased parasympathetic nervous system by HRV in irritable bowel syndrome with diarrhea as a predominant symptom
- 1.Aggarwal A, Cutts TF, Abell TL, Cardoso S, Familoni B, Bremer J, et al. Predominant symptoms in irritable bowel syndrome correlate with specific autonomic nervous system abnormalities. Gastroenterology 1994;106:945–50.ArticlePubMed
- 2.Luczak H, Laurig W. An analysis of heart rate variability. Ergonomics 1973;16:85–97.ArticlePubMed
- 3.Liu J, Hou X. A review of the irritable bowel syndrome investigation on epidemiology, pathogenesis and pathophysiology in China. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2011;26:88l–93.Article
- 4.Barclay GR, Turnberg LA. Effect of psychological stress on salt and water transport in the human jejunum. Gastroenterology 1987;93:91–7.ArticlePubMed
- 5.Taylor CT, Keely SJ. The autonomic nervous system and inflammatory bowel disease. Auton Neurosci 2007;133:104–14.ArticlePubMed
- 6.Evans PR, Bak YT, Shuter B, Hoschl R, Kellow JE. Gastroparesis and small bowel dysmotility in irritable bowel syndrome. Dig Dis Sci 1997;42:2087–93.PubMed
- 7.Arad M, Abboud S, Radai MM, Adunsky A. Heart rate variability parameters correlate with functional independence measures in ischemic stroke patients. J Electrocardiol 2002;35:243–6.ArticlePubMed
- 8.Hon EH LS. Electronic evaluations of the fetal heart rate patterns preceding fetal death, further observations. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1963;87:814–26.PubMed
- 9.Aronson D, Mittleman MA, Burger AJ. Measures of heart period variability as predictors of mortality in hospitalized patients with decompensated congestive heart failure. Am J Cardiol 2004;93:59–63.ArticlePubMed
- 10.Vinik AI, Maser RE, Mitchell BD, Freeman R. Diabetic autonomic neuropathy. Diabetes Care 2003;26:1553–79.ArticlePubMed
- 11.Jeong KS. The outline of HRV. J Korean Acad Fam Med 2004;25:S528–32.
- 12.Heart rate variability: standards of measurement, physiological interpretation and clinical use. Task Force of the European Society of Cardiology and the North American Society of Pacing and Electrophysiology. Circulation 1996;93:1043–65.PubMed
References
Figure & Data
References
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by 

- Sound stimulation using the individual's heart rate to improve the stability and homeostasis of the autonomic nervous system
Daechang Kim, Nahyeon Kim, Younju Lee, Sungmin Kim, Jiyean Kwon
Physiological Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - A Study on Resonance Sound Stimulation Using an Individual's Heart Rate to Improve the Stability and Homeostasis of the Autonomic Nervous System
kim daechang, Seungbong Lee, Jaehoon Jeong, Sung Min Kim
SSRN Electronic Journal .2022;[Epub] CrossRef

 KOSIN UNIVERSITY COLLEGE OF MEDICINE
KOSIN UNIVERSITY COLLEGE OF MEDICINE


 PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Cite
Cite