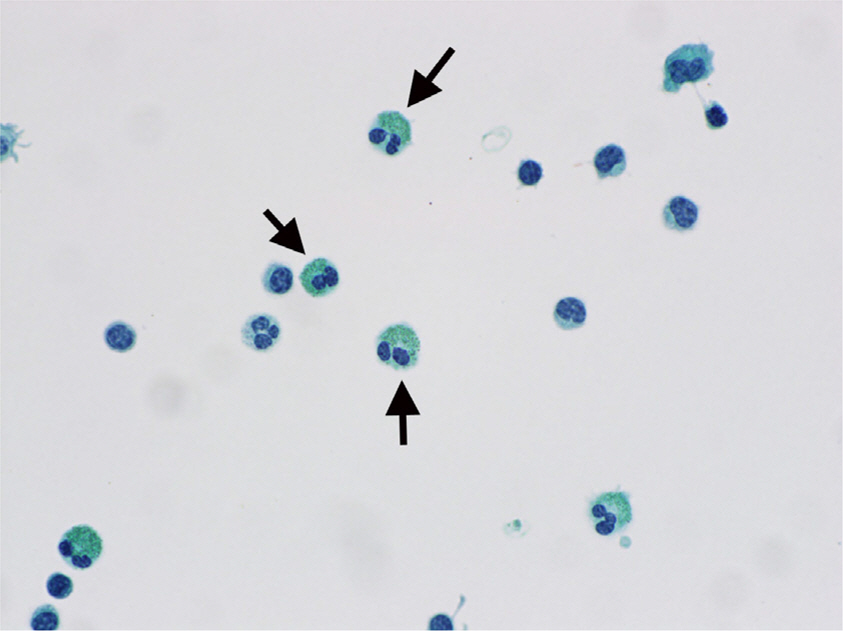
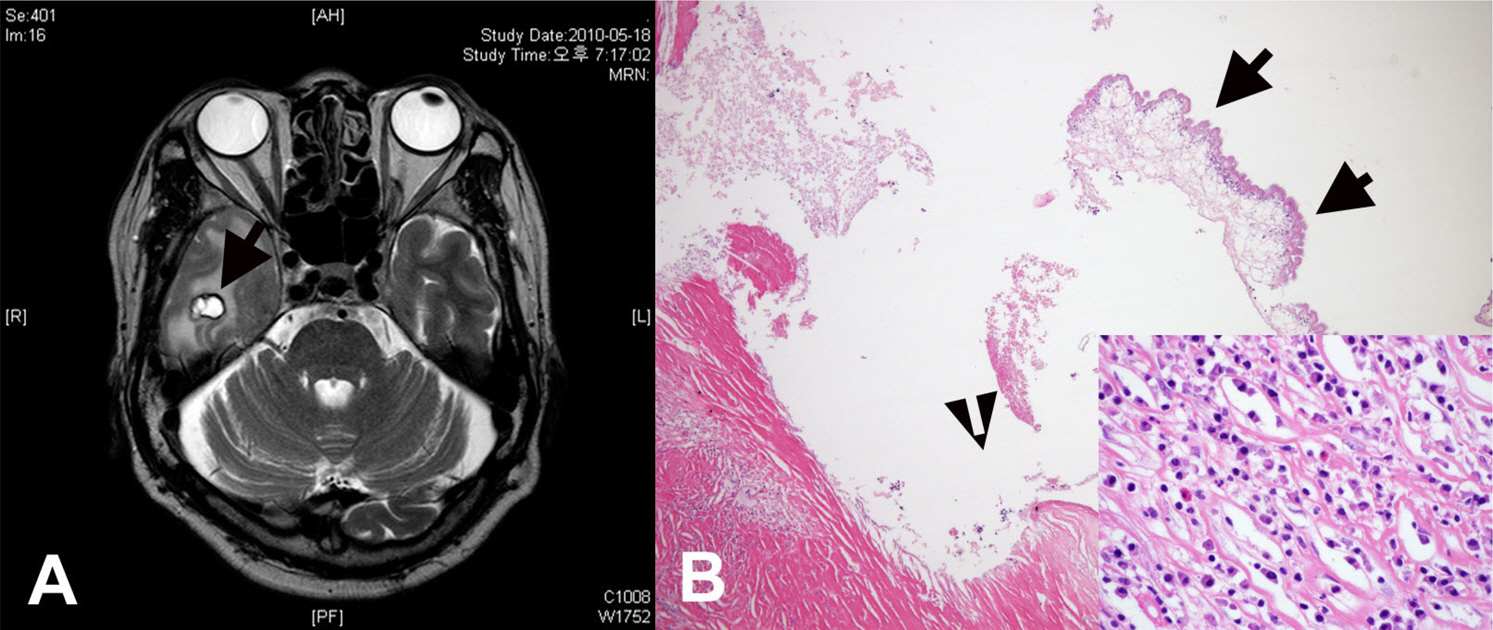
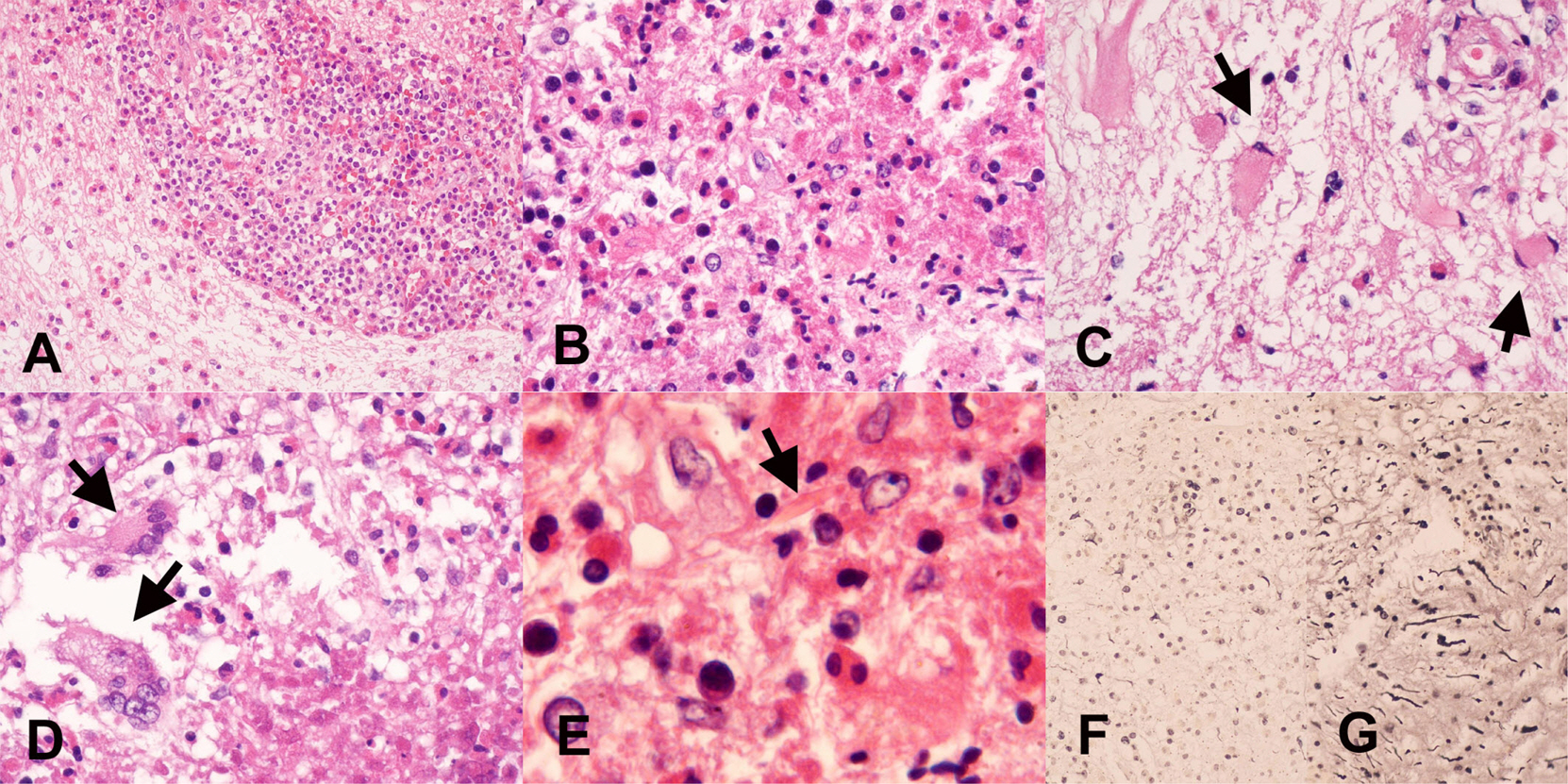
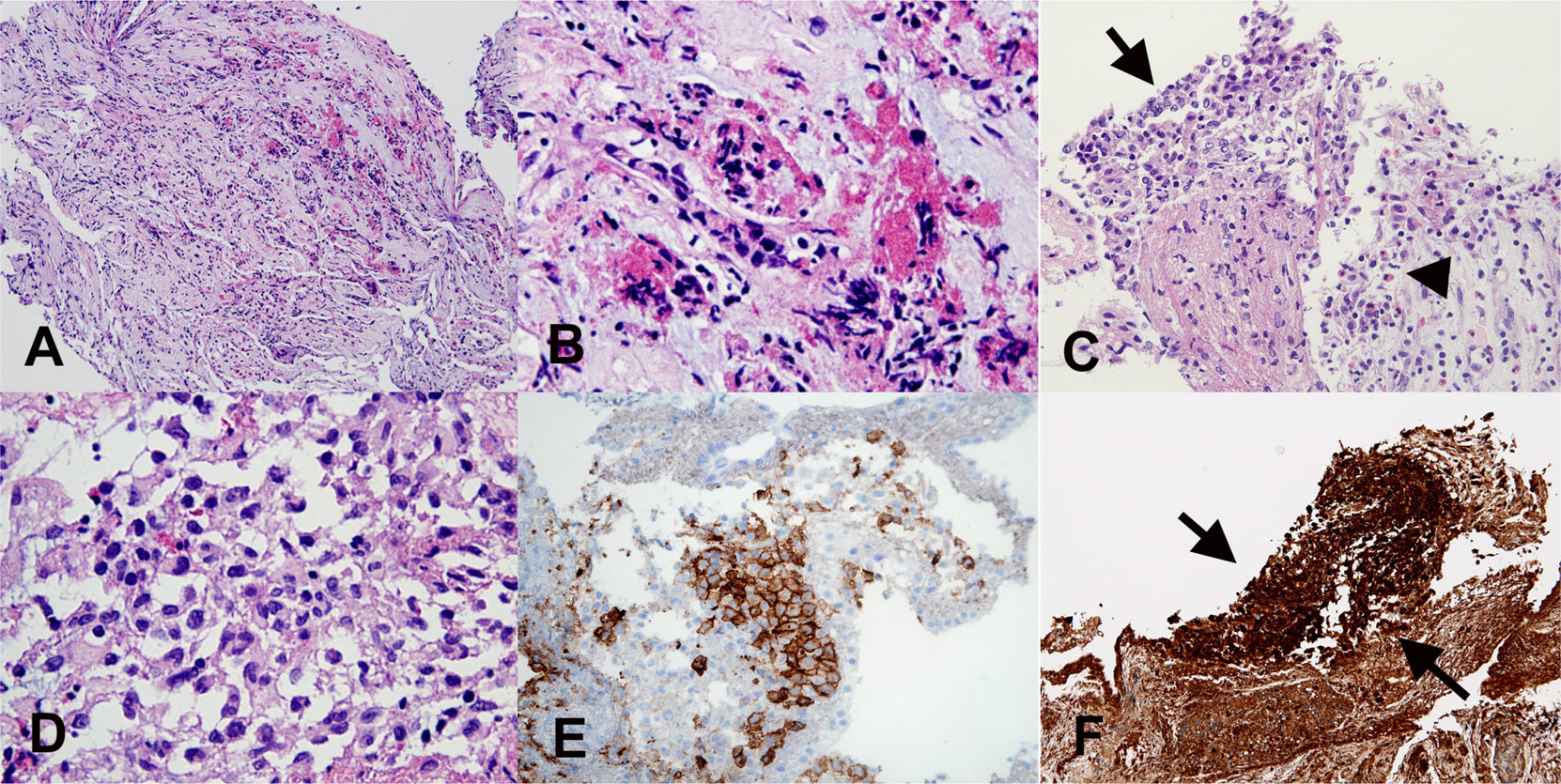
References
1. Young B. Wheater's functional histology: a text and colour atlas 5th ed.th ed. Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone/Elsevier; 2006.
2. Curran CS, Bertics PJ. Eosinophils in glioblastoma biology. J Neuroinflammation 2012;9:11.
3. Seehusen DA, Reeves MM, Fomin DA. Cerebrospinal fluid analysis. Am Fam Physician 2003;68:1103–8.
4. Ramzy I. Clinical cytopathology and aspiration biopsy: Fundamental principles and practice 2nd ed.th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill; 2001.
5. Luna LG. The quality control dilemma in Histotechnology: A possible answer. Histologic 1991;21:245–50.
6. Goffette S, Jeanjean AP, Duprez TP, Bigaignon G, Sindic CJ. Eosinophilic pleocytosis and myelitis related to Toxocara canis infection. Eur J Neurol 2000;7:703–6.
7. Harzheim M, Schlegel U, Urbach H, Klockgether T, Schmidt S. Discriminatory features of acute transverse myelitis: a retrospective analysis of 45 patients. J Neurol Sci 2004;217:217–23.
8. Jeffery DR, Mandler RN, Davis LE. Transverse myelitis. Retrospective analysis of 33 cases, with differentiation of cases associated with multiple sclerosis and parainfectious events. Arch Neurol 1993;50:532–5.
9. Kawamura J, Kohri Y, Oka N. Eosinophilic meningoradiculo- myelitis caused by Gnathostoma spinigerum. A case report. Arch Neurol 1983;40:583–5.
10. Kerr DA, Ayetey H. Immunopathogenesis of acute transverse myelitis. Curr Opin Neurol 2002;15:339–47.
11. Kikuchi H, Osoegawa M, Ochi H, Murai H, Horiuchi I, Takahashi H, et al. Spinal cord lesions of myelitis with hyperIgEemia and mite antigen specific IgE (atopic myelitis) manifest eosinophilic inflammation. J Neurol Sci 2001;183:73–8.
12. Tsai CP, Yeh HH, Tsai JJ, Lin KP, Wu ZA. Transverse myelitis and polyneuropathy in idiopathic hypereosinophilic syndrome. Muscle Nerve 1993;16:112–3.
13. Kira J, Yamasaki K, Kawano Y, Kobayashi T. Acute myelitis associated with hyperIgEemia and atopic dermatitis. J Neurol Sci 1997;148:199–203.
14. Kira J, Kawano Y, Yamasaki K, Tobimatsu S. Acute myelitis with hyperIgEaemia and mite antigen specific IgE: atopic myelitis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 1998;64:676–9.
15. Osoegawa M, Ochi H, Kikuchi H, Shirabe S, Nagashima T, Tsumoto T, et al. Eosinophilic myelitis associated with atopic diathesis: a combined neuroimaging and histopathological study. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 2003;105:289–95.
16. Osoegawa M, Ochi H, Minohara M, Murai H, Umehara F, Furuya H, et al. Myelitis with atopic diathesis: a nationwide survey of 79 cases in Japan. J Neurol Sci 2003;209:5–11.
17. Lucchinetti CF, Mandler RN, McGavern D, Bruck W, Gleich G, Ransohoff RM, et al. A role for humoral mechanisms in the pathogenesis of Devic's neuromyelitis optica. Brain 2002;125:1450–61.
18. Milici AJ, Carroll LA, Stukenbrok HA, Shay AK, Gladue RP, Showell HJ. Early eosinophil infiltration into the optic nerve of mice with experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. Lab Invest 1998;78:1239–44.
19. Giannini C, Salvarani C, Hunder G, Brown RD. Primary central nervous system vasculitis: pathology and mechanisms. Acta Neuropathol 2012;123:759–72.
20. Nordborg E, Nordborg C. Giant cell arteritis. In : Kalimo H, ed. editor. Pathology & Genetics Cerebrovascular Diseases Basel: International Society of Neuropathology; 2005. p. 134–9.
21. Bazile C, Keohane C, Gray F. Systemic Diseases and Drug-Induced Vasculitis. In : Kalimo H, ed. editor. Pathology & Genetics Cerebrovascular Diseases Basel: International Society of Neuropathology; 2005. p. 151–62.
22. Guillevin L, Cohen P, Gayraud M, Lhote F, Jarrousse B, Casassus P. Churg-Strauss syndrome. Clinical study and long-term follow-up of 96 patients. Medicine 1999;78:26–37.
23. Na SJ, Lee KO, Ko JH. Eosinophilic vasculitis of the spinal cord associated with Churg-Strauss syndrome. J Neurol Sci 2010;295:107–9.
24. Jennette JC, Falk RJ. Small-vessel vasculitis. N Engl J Med 1997;337:1512–23.
25. Kono H, Inokuma S, Nakayama H, Yamazaki J. Pachymeningitis in microscopic polyangiitis (MPA): a case report and a review of central nervous system involvement in MPA. Clin Exp Rheumatol 2000;18:397–400.
26. Furukawa Y, Matsumoto Y, Yamada M. Hypertrophic pachymeningitis as an initial and cardinal manifestation of microscopic polyangiitis. Neurology 2004;63:1722–4.
27. Huang CH, Hung CH, Chu YT, Hua YM. Tumor-like cerebral perivasculitis in a pediatric patient with systemic lupus erythematosus. Kaohsiung J Med Sci 2008;24:218–22.
28. Moezzi J, Gopalswamy N, Haas RJ Jr, Markert RJ, Suryaprasad S, Bhutani MS. Stromal eosinophilia in colonic epithelial neoplasms. Am J Gastroenterol 2000;95:520–3.
29. Kural YB, Su O, Onsun N, Uras AR. Atopy, IgE and eosinophilic cationic protein concentration, specific IgE positivity, eosinophil count in cutaneous T Cell lymphoma. Int J Dermatol 2010;49:390–5.
30. Iwasaki K, Torisu M, Fujimura T. Malignant tumor and eosinophils. I. Prognostic significance in gastric cancer. Cancer 1986;58:1321–7.
31. Dorta RG, Landman G, Kowalski LP, Lauris JR, Latorre MR, Oliveira DT. Tumour-associated tissue eosinophilia as a prognostic factor in oral squamous cell carcinomas. Histopathology 2002;41:152–7.
32. Moroni M, Porta C, De Amici M, Quaglini S, Cattabiani MA, Buzio C. Eosinophils and C4 predict clinical failure of combination immunotherapy with very low dose subcutaneous interleukin-2 and interferon in renal cell carcinoma patients. Haematologica 2000;85:298–303.
33. Cormier SA, Taranova AG, Bedient C, Nguyen T, Protheroe C, Pero R, et al. Pivotal Advance: eosinophil infiltration of solid tumors is an early and persistent inflammatory host response. J Leukoc Biol 2006;79:1131–9.
34. Sherman PW, Holland E, Sherman JS. Allergies: their role in cancer prevention. Q Rev Biol 2008;83:339–62.
35. Mueller MM, Herold-Mende CC, Riede D, Lange M, Steiner HH, Fusenig NE. Autocrine growth regulation by granulocyte colony-stimulating factor and granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor in human gliomas with tumor progression. Am J Pathol 1999;155:1557–67.
36. Curran CS, Evans MD, Bertics PJ. GM-CSF production by glioblastoma cells has a functional role in eosinophil survival, activation, and growth factor production for enhanced tumor cell proliferation. J Immunol 2011;187:1254–63.
37. Smith D, Shimamura T, Barbera S, Bejcek BE. NF-kappaB controls growth of glioblastomas/astrocytomas. Mol Cell Biochem 2008;307:141–7.
38. Ranza E, Facoetti A, Morbini P, Benericetti E, Nano R. Exogenous platelet derived growth factor (PDGF) induces human astrocytoma cell line proliferation. Anticancer Res 2007;27:2161–6.